

The Oxygens each have eight valence electrons, but the central Nitrogen only has six. We've used 4, then around the Oxygen atoms, 6, 16, and then back to the central Nitrogen, 18. We'll put two between atoms to form chemical bonds. Nitrogen is the least electronegative, we'll put that in the center and we'll put the Oxygens on either side.
#NITRATE ION LEWIS STRUCTURE CHEMDOODLE PLUS#
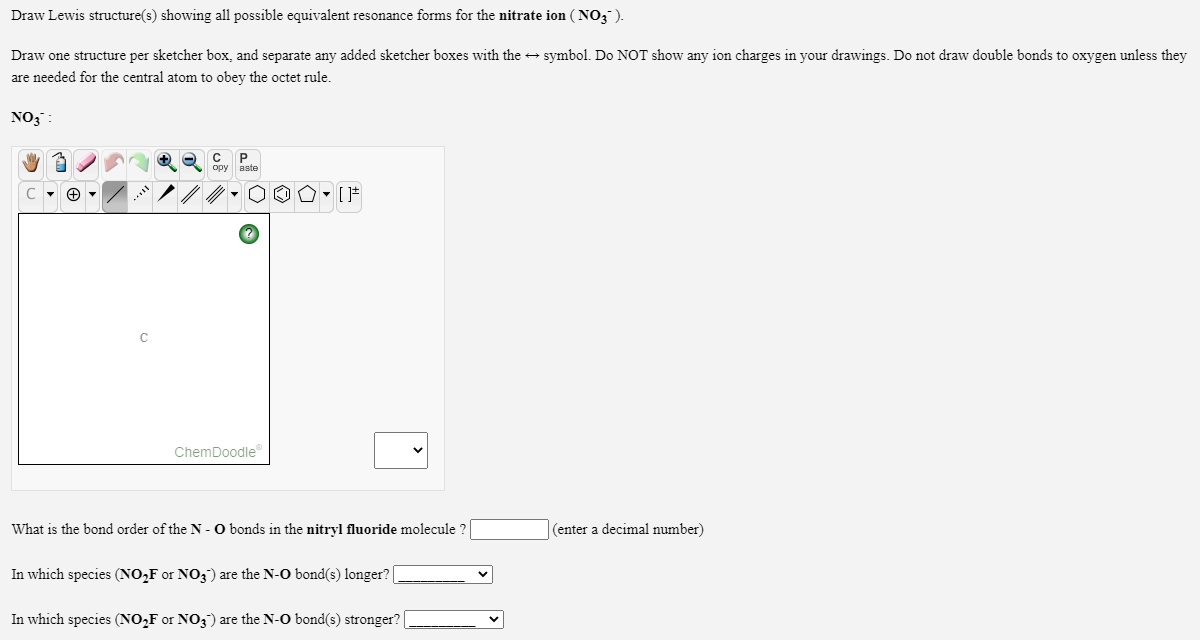
For Nitrogen we have 5 valence electrons 6 for Oxygen, but we have two Oxygens so we'll multiply that by two plus one for this valence electron up here gives us a total of 18 valence electrons for the NO2- Lewis structure. “Nitrate ion resonance structures” (CC BY-SA 3.Transcript: This is the NO2- Lewis structure: the nitrite ion.
“Nitrogen Cycle 1” By Eme Chicano – Own work (CC0) via Commons Wikimediaģ. “Electron shell 007 Nitrogen” By Pumbaa (original work by Greg Robson) – File:Electron shell 007 nitrogen.png, (CC BY-SA 2.0 uk) via Commons WikimediaĢ.

National Library of Medicine, Available here. “Nitrate.” National Center for Biotechnology Information. “Nitrogen.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 2 Dec. “Nitrogen – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table.” Royal Society of Chemistry – Advancing excellence in the chemical sciences, Available here.Ģ. The main difference between nitrogen and nitrate is that nitrogen is a chemical element whereas nitrate is an anion. Nitrogen can be found circulating in the nitrogen cycle in different forms whereas nitrate ion can be found in the steps of nitrification and denitrification. Nitrate ion is an anion having -1 electrical charge. Nitrate:Nitrate ion can be found in salts and in covalent compounds. Nitrogen: Nitrogen forms a wide range of different compounds including inorganic compounds and organic compounds. Nitrate:Nitrifying bacteria in nitrogen cycle converts ammonium ion into nitrate ion whereas denitrifying bacteria convert nitrate ion into nitrogen gas. Nitrogen:Nitrogen element circulates in the nitrogen cycle in different forms such as ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate. Nitrogen:A nitrogen atom has no net electrical charge. Nitrogen: Nitrogen is a chemical element. Nitrate:Nitrate is an anion having the chemical formula NO 3 –. Nitrogen: Nitrogen is a chemical element in the group 15 of the periodic table and has the chemical symbol “N.” Difference Between Nitrogen and Nitrate Definition But denitrifying bacteria (such as Pseudomonas) can convert nitrate into nitrogen gas. In the nitrogen cycle, nitrifying bacteria ( Nitrobacter) converts nitrite ions into nitrate ions. Covalent compounds of nitrate include esters of nitric acid. Salts of nitrate are ionic compounds composed of nitrate ion bonded to a cation. Some examples include ammonium nitrate, sodium nitrate, potassium nitrate, etc. Nitrate salts are common on earth as mineral deposits.
#NITRATE ION LEWIS STRUCTURE CHEMDOODLE FREE#
Nitrate ion can be found in ionic compounds as salts, and as a free aqueous ion. For example, nitrobenzene is synthesized by reacting benzene with a mixture of nitric acid, sulfuric acid, and water. Nitric acid is a key ingredient for most synthesis reactions in organic chemistry. When nitrate ion is bonded to a proton, it is called nitric acid. At room temperature and standard pressure, nitrogen exists as a diatomic gaseous compound which is colorless, odorless and tasteless.įigure 2: Resonance Structures of Nitrate Ion The atomic number of nitrogen is 7, and the relative atomic mass is about 14 amu. Nitrogen is a chemical element in the group 15 of the periodic table and has the chemical symbol “N.” Nitrogen is a p block element according to its electron configuration 2s 22p 3. Key Terms: Amides, Ammines, Anion, Cation, Covalent, Nitrate, Nitrogen, Nitrogen Cycle, Oxygen, Relative Atomic Mass, Resonance

What is the Difference Between Nitrogen and Nitrate Nitrate ions can form different salt compounds by combining with different cations and covalent compounds such as esters of nitric acid. Nitrate is one such ion in which a nitrogen atom is bonded to three oxygen atoms forming an anion. It can form different types of molecules and ions by combining with different other elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, etc. Nitrogen is a chemical element in the group 15 of the periodic table.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
